Home office at full pay is not an option for all employees hit by the coronavirus crisis. To analyze changes in work arrangements during the pandemic, a team of economists from the University of Bonn, IZA and the University of Tilburg surveyed around 5,500 individuals in the Netherlands from March 20-31. The results show that high-skilled workers spend more time in the home office, while less-skilled workers are more likely to work reduced hours or lose their jobs.
Education plays a key role in terms of being able to work from home, according to new data from the COVID Impact Lab, a joint research project by the University of Bonn’s ECONtribute Cluster of Excellence and IZA. The researchers compared work arrangements at the onset of the crisis and shortly after social-distancing policies were implemented. Their data are the first to show detailed changes in the proportion of telework among different groups of employees.
High-paid workers benefit from the home office option
The total share of employees who work from home at least two hours a day has doubled from 27 to 54 percent. This is mainly driven by high-skilled workers (76 percent) while only 31 percent of low-skilled workers report at least two home office hours per week since the beginning of the crisis. For university graduates, switching to telecommuting seems relatively easy: While their share of home office hours increased from 11 to 68 percent, the share among the low-educated is only one-fifth. The latter group, instead, experienced a much larger drop in total hours (see Figure 1).
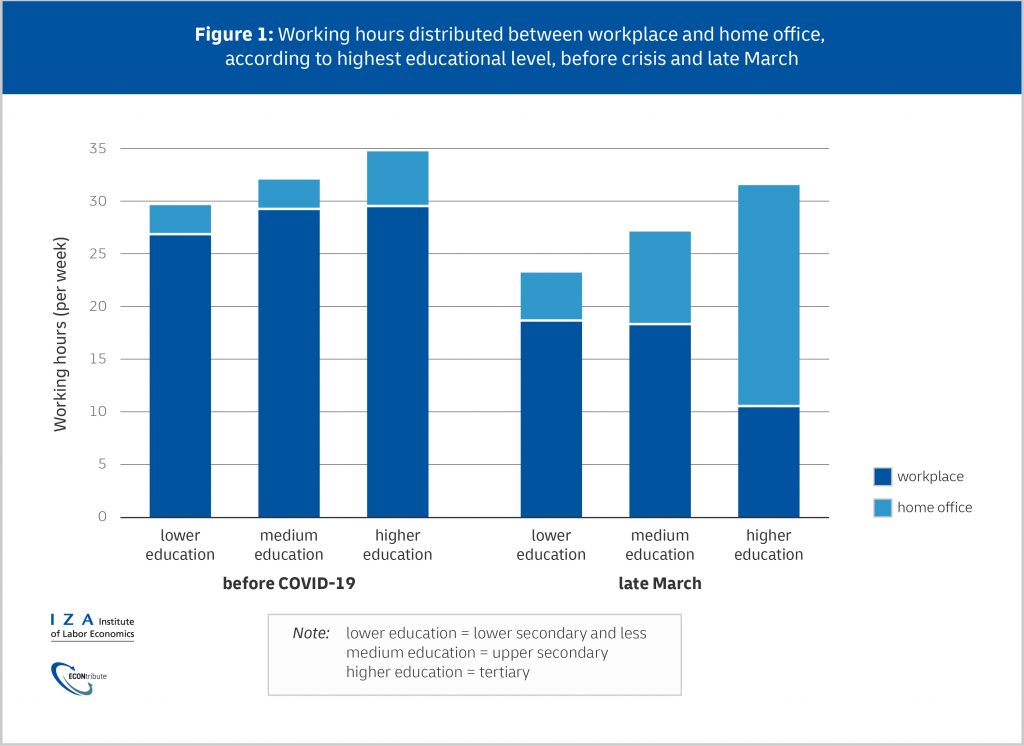
Double impact of the crisis on low-income earners
The main reason may be that less qualified workers are more often found in occupations where remote work is impossible, such as transportation, retail, or catering. This makes them more prone to job loss or substantial working hour reductions. At the same time, they are less likely to have savings or assets to compensate for income loss, which makes them particularly vulnerable to the crisis and more in need of government support.
Lower educated workers are also found in essential occupations, such as nursing care or grocery retailing. While their jobs are currently safe, they are at higher risk of infection. Home office workers, on the other hand, are protected against both infection and income loss. This aggravates the labor market segmentation into office jobs, characterized by higher education levels and home office rates, and lower-skilled jobs with no home office option (see Figure 2).
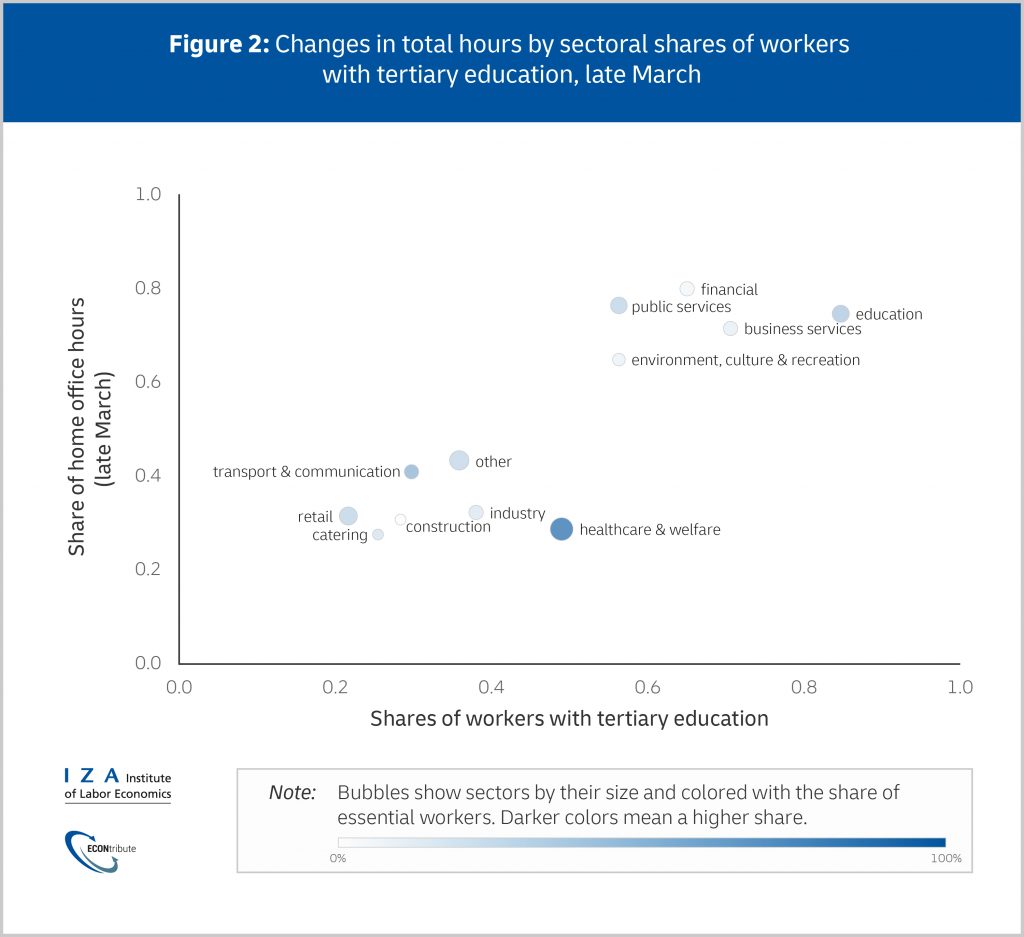
Transferability of the findings to Germany
“The data currently available for Germany are less detailed, but preliminary findings suggest that the situation is very similar. Although the increase in the share of home office hours seems somewhat less pronounced than in the Netherlands, it is clear that workers without higher education are less likely to be able to work from home. Both countries have also implemented similar restrictions on social contacts, which creates a comparable setting,” says IZA research team leader and ECONtribute professor Hans-Martin von Gaudecker.
About the dataset
Data were collected through the Dutch LISS panel (Longitudinal Internet Studies for the Social Sciences) which has been surveying 4,500 households regularly on a variety of topics for over ten years. The households are representative of the Dutch population and answer the questionnaires online. For the current wave of the LISS panel, the research team designed a new module to ask panel members about behaviors, beliefs and expectations during the Corona epidemic. The first wave of this module was fielded between March 20 and March 31 among LISS participants aged 16 and over. The response rate was over 80 percent, which translates into a sample of 5,544 individuals. Comprehensive data are not yet available for Germany, but initial trends can be seen. The German data is also being collected via an online survey through GESIS, the Leibniz Institute for the Social Sciences.
